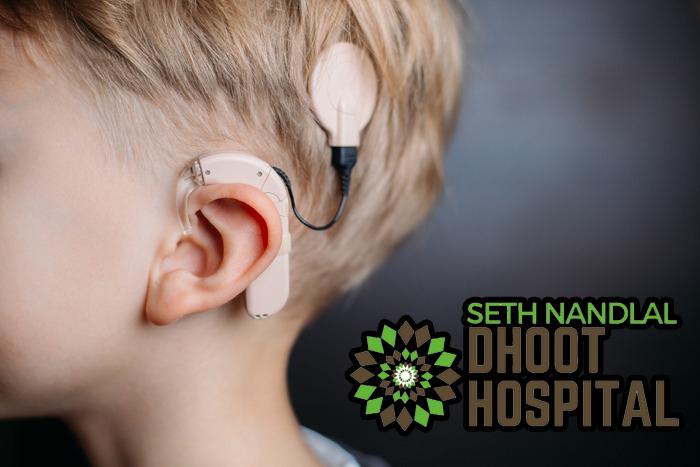
The cochlea is the spiral-shaped cavity that is present inside the inner ear, this cavity looks like a snail shell and contains nerve endings crucial for hearing. A cochlear implant is a small electronic device that helps to provide a sense of sound and partially restore hearing. People with severe hearing loss and inner ear damage can opt for cochlear implants.
Generally, hearing aids only amplify the sound but a cochlear implant makes sure to avoid the damaged part of the ear and deliver signals to the hearing nerves.
The cochlear implant consists of a sound processor and a receiver. The sound processor is placed behind the ear that captures and sends sound signals to the receiver which is implanted under the skin behind the ear. The receiver then sends signals to the electrodes that are implanted in the inner ear also known as the cochlea.
These signals invigorate the hearing nerves and direct them to the brain. The signals are then construed by the brain as sound signals. These sounds are not like normal hearing, it takes a considerable amount of time to learn to construe the signals received from the implant.
Why Cochlear Implant is done?
People with severe hearing loss who can no longer be helped by hearing aids can get cochlear implantation to restore their hearing. A cochlear implant can also improve their communication.
Cochlear implants can be unilateral or bilateral meaning they can be placed in one ear or both ears depending on the seriousness of the hearing loss. To treat infants and children from bilateral hearing loss there is an increase in the use of the cochlear implant in both ears.
People with cochlear implants have reported the following improvements:
- There is no need to follow any visual cues to hear speech.
- Able to interpret normal and environmental sounds
- Improved hearing as listening in a noisy environment is no longer an issue
- You can understand from where the sound is coming
Who can have Cochlear Implants?
The criteria for have a cochlear implant are as follows:
Severe hearing loss that does not let you communicate properly
The use of hearing aids are no longer an option
You should have no medical conditions which can cause complications with the cochlear implant
Request an appointment at Seth Nandlal Dhoot Hospital Ltd, Chhatrapati Sambhajinagar (Aurangabad)
What are the risks?
Generally, the procedure is very safe. Some of the risks are:
- Bleeding
- Device failure
- Infection
- Balance problem
- Taste disturbance, etc.
Before the operation
You will be thoroughly examined by your doctor to determine whether the implants are a good or bad option for you. Your doctor may conduct the following tests:
Your hearing, balance, and speech will be tested.
A physical examination will be performed to check your inner ear’s health.
MRI or CT scan will be performed to check the condition of the cochlea.
You will be told to stop taking certain medications before the surgery and also to avoid eating and drinking.
During the Operation
At first, you will be given general anesthesia to put you in a controlled state of unconsciousness. Then a small incision will be made behind your ear and form a small hole to place the internal device. Once placed the incision is closed.
After the Operation
Normally, you or your child may experience the following:
Dizziness
Discomfort in or around the ear
The device is activated two to six weeks after the surgery as the operated area needs to be completely healed.
How to Activate the Cochlear Implant
To activate the implant, an audiologist will do the following steps:
- The doctor will adjust the sound processor according to you.
- Check all the components and their state.
- Will give you information’s on how to take care of the device and keep it safe.
- Set the devices according to you so that you can hear properly.
Conclusion
Cochlear surgery is very safe and is recommended to people who are suffering from severe hearing loss. The surgery varies from person to person depending on their condition, age, etc. Children with hearing loss should get cochlear surgery done at a young age. Some benefits and positive outcomes are clear hearing, better communication, etc.