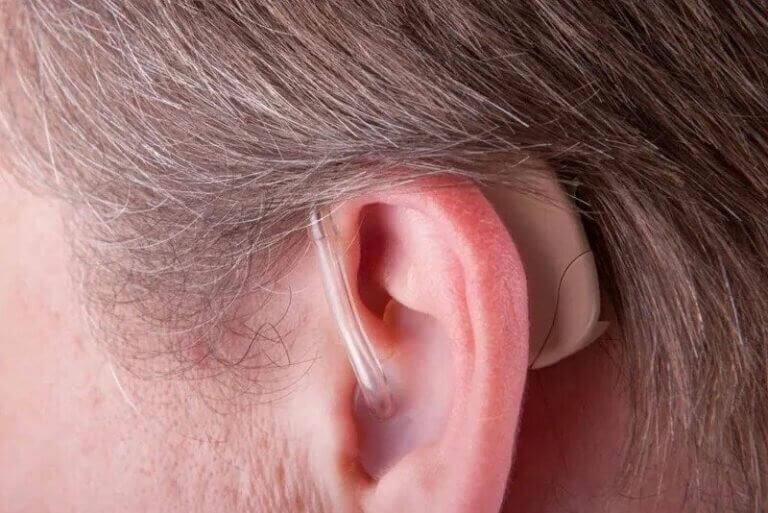
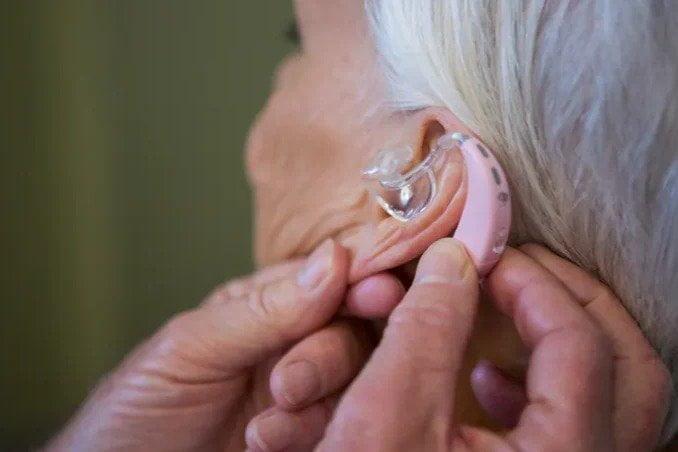
Invisible. Rechargeable. Modern Hearing Aids
Hearing Aid Styles
Why Choose Vr Speech And Hearing Clinic as a Hearing aids consultant:
- Get trial for latest in Digital Hearing Aid technology for free.
- Enjoy lifetime after-sales service, absolutely free of charge.
- Free Home Visits available for senior citizen
- Cutting-Edge Technology: They stay updated with the latest advancements in hearing aid technology, ensuring you have access to the most advanced and effective devices available.
- Affordable Options: VR Speech and Hearing Clinic works to accommodate various budgets, providing cost-effective solutions without compromising on quality.
- Positive Reputation: With a history of success and satisfied clients, VR Speech and Hearing Clinic has built a strong reputation for delivering exceptional hearing healthcare services.
- Get trial with different ear machine brands, certified quality hearing aid products and excellent technical & personal support.
- Meet Our Best Audiologists.




Hearing Aid Price in India starts from ₹14,999 and goes up to ₹7,09,990. Hearing aids offer an excellent combination of quality and affordability, making them an attractive choice for individuals seeking reliable and cost-effective solutions for their hearing needs in India. These hearing machines are designed to deliver exceptional performance, allowing you to enjoy clear and natural sound in various listening environments.
In-the-ear (ITE) hearing aids
In-the-ear (ITE) hearing aids are small, discreet devices that fit directly into the ear canal, allowing for improved sound quality and amplifying capabilities.
Here are the benefits of ITE hearing aids:
- They provide improved sound quality and amplifying capabilities.
- They come in different skin tones to blend in with your natural ear shape.
Behind-the-ear (BTE) hearing aids
Behind-the-ear (BTE) hearing aids are an effective solution to hearing loss. These devices are mounted behind or on top of the ear.
Typically, BTE hearing aids require:
- Custom-fit ear molds or a dome style that do not block the ear canal opening.
- Batteries, either rechargeable (like smartphones) or disposable, which need to be replaced every 3-20 days.
IIC & CIC hearing aid:
IIC & CIC hearing aids are the smallest and most discreet in size. IIC is smaller than CIC and is inserted deeply into the ear canal, requiring a string for easy removal.
- Small and discreet size
- Good Sound quality and close fit in canal.
In-the-canal (ITC) hearing aids
In-the-canal (ITC) hearing aids are also small and discreet sit in the lower portion of the outer ear bowl. They are also comfortable and easy to use.
Advantages of In-the-canal Hearing Aids:
- Discreet small in size
- Longer Battery Life and More Features than IIC and CIC styles
RIC Hearing aids
Receiver in Canal (RIC) hearing aids are popular among those with hearing loss. It has a speaker/ receiver that is inserted into the ear canal and the body sits on top of the ear.
Benefits of RIC Hearing aid:
- Wireless connectivity to phones or other devices
- Speaker can be replaced separately
- Easy to find options with rechargeable batteries
Visit Near By Vr Speech And Hearing Clinic | Ahilynagar | Ahmednagar | Auranagabad | Chh. Sambhajinagar | Beed | Pune |
Make Online Order All Over Maharashtra | Akola | Amravati | Aurangabad | Beed | Bhandara | Buldhana | Chandrapur | Dhule | Gadchiroli | Gondia | Hingoli | Jalgaon | Jalna | Kolhapur | Latur | Mumbai City | Mumbai Suburban | Nagpur | Nanded | Nandurbar | Nashik | Osmanabad | Palghar | Parbhani | Pune | Raigad | Ratnagiri | Sangli | Satara | Sindhudurg | Solapur | Thane | Wardha | Washim | Yavatmal |